Crypto Staking 2025: Beginner Guide
Learn how crypto staking works, explore different staking methods, understand risks and rewards, and discover the best platforms to start earning passive income in 2025.
Introduction
Cryptocurrency staking has emerged as one of the most popular and accessible ways to earn passive income in the digital asset space. As blockchain networks continue to evolve from energy-intensive proof-of-work systems to more sustainable proof-of-stake mechanisms, staking has become a cornerstone of the modern crypto ecosystem, fundamentally transforming how investors participate in blockchain networks whilstearning rewards.
In 2025, the staking landscape offers unprecedented opportunities for both beginners and experienced investors. With over $150 billion worth of cryptocurrency currently staked across various networks, the market has matured significantly, providing diverse options ranging from simple centralised platforms to sophisticated decentralised protocols that cater to different risk profiles and investment strategies.
The evolution of staking mechanisms has created multiple pathways for participation, from traditional validator staking that requires technical expertise and significant capital commitments to liquid staking solutions that enable smaller investors to participate while maintaining liquidity. This democratisation of staking has made it possible for virtually any cryptocurrency holder to earn rewards by contributing to network security and consensus mechanisms.
Professional staking strategies have become increasingly sophisticated, incorporating risk management techniques, diversification across multiple networks, and advanced yield optimisation methods that institutional investors use to maximise returns while managing exposure to slashing risks and market volatility. The most successful stakers understand the importance of validator selection, network governance participation, and strategic timing of staking and unstaking activities.
The evolution of staking represents a paradigm shift in blockchain technology, moving away from energy-intensive mining towards more sustainable consensus mechanisms. This transition has democratised network participation, allowing ordinary users to contribute to blockchain security whilstearning predictable returns on their cryptocurrency holdings without requiring expensive hardware or technical expertise.
Understanding staking is crucial for anyone serious about cryptocurrency investing in 2025. Unlike traditional trading strategies that rely on market timing and price speculation, staking provides a more stable approach to generating returns through network participation. This fundamental difference has made staking an essential component of modern cryptocurrency portfolios, offering both diversification benefits and steady income streams.
This comprehensive guide will take you through everything you need to know about crypto staking in 2025. Whether you're a complete beginner looking to understand the basics or an experienced investor seeking advanced strategies, you'll find practical insights, detailed platform comparisons, and actionable advice to help you make informed decisions about your staking journey and maximise your returns while managing risks effectively.
We'll explore how staking works at a technical level, examine different types of staking available today, analyse the risks and rewards involved, and provide detailed reviews of the best staking platforms currently available. Additionally, we'll cover advanced topics including liquid staking derivatives, validator selection criteria, slashing risks, and tax implications to ensure you have complete understanding of the staking ecosystem.
The staking market in 2025 is characterised by increased innovation, with new protocols launching regularly and existing platforms continuously improving their offerings. From Ethereum's successful transition to proof-of-stake to the emergence of liquid staking derivatives and restaking protocols, the opportunities for earning yield on cryptocurrency holdings have never been more diverse, accessible, or sophisticated.
By the end of this guide, you'll have a thorough understanding of crypto staking and be equipped with the knowledge needed to start your own staking journey confidently. We'll provide step-by-step instructions for getting started, share best practices for security and risk management, and help you choose the right staking strategy based on your goals, risk tolerance, and technical expertise level.
What is Crypto Staking?
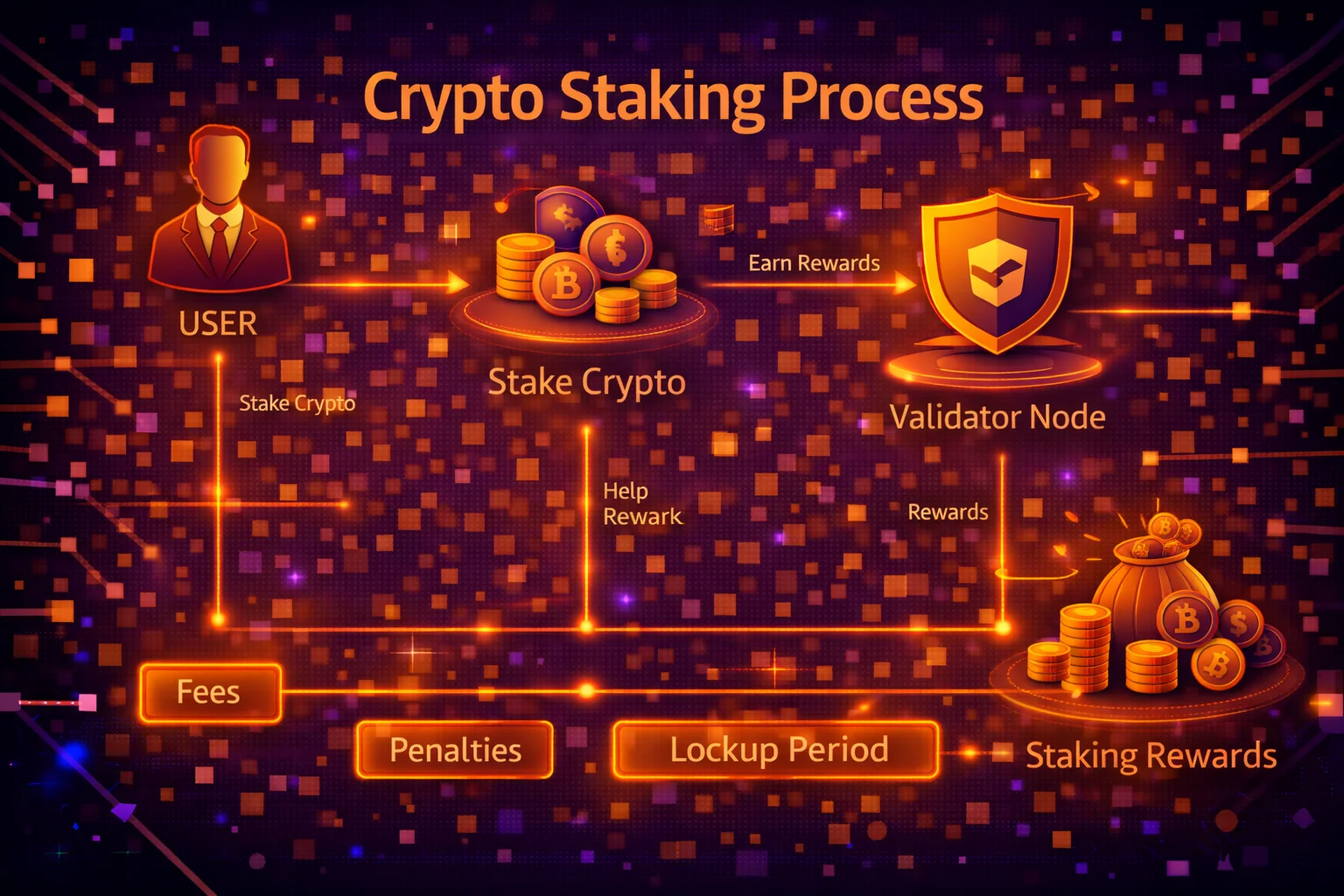
Crypto staking is the process of participating in a proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain network by locking up your cryptocurrency to help validate transactions and secure the network. In return for this service, you earn rewards in the form of additional cryptocurrency tokens.
Think of staking as earning interest on your crypto holdings while contributing to the network's security and decentralisation. Unlike proof-of-work systems like Bitcoin that require energy-intensive mining, proof-of-stake networks rely on validators who "stake" their tokens as collateral to process transactions.
The Evolution from Mining to Staking
Staking represents a fundamental shift in how blockchain networks achieve consensus:
- Proof-of-Work (Bitcoin): Miners compete using computational power to solve cryptographic puzzles
- Proof-of-Stake (Ethereum 2.0): Validators are chosen to create blocks based on their stake size and other factors
- Delegated Proof-of-Stake (Cosmos): Token holders vote for validators who secure the network on their behalf
This transition offers several advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: 99.95% less energy consumption compared to mining
- Lower Barriers: No need for expensive mining hardware
- Passive Income: Earn rewards simply by holding and staking tokens
- Network Security: Economic incentives align validators with network health
Key Staking Concepts
Validators: Network participants who propose and validate new blocks
Delegators: Token holders who delegate their stake to validators
Slashing: Penalty mechanism for malicious or negligent validator behavior
Unbonding Period: Time required to withdraw staked tokens
APY (Annual Percentage Yield): Expected yearly return from staking
How Staking Works: The Technical Process
The Validator Selection Process
In proof-of-stake networks, validators are chosen to propose new blocks through various mechanisms:
Randomized Selection
Most PoS networks use pseudo-random selection algorithms that consider:
- Stake Size: Larger stakes increase selection probability
- Coin Age: How long tokens have been staked
- Randomization: Prevents predictable patterns
Block Validation Process
- Selection: Algorithm chooses a validator to propose the next block
- Proposal: Selected validator creates a block with pending transactions
- Attestation: Other validators verify and vote on the proposed block
- Finalization: Block is added to the blockchain once consensus is reached
- Rewards: Participating validators receive rewards for their work
Reward Distribution Mechanisms
Staking rewards come from multiple sources:
Block Rewards
New tokens created by the protocol and distributed to validators. These are typically:
- Fixed: Predetermined amount per block (like Cardano)
- Variable: Adjusted based on network conditions (like Ethereum)
- Inflationary: Increase total token supply
- Deflationary: Some networks burn tokens to offset inflation
Transaction Fees
Validators earn fees from transactions they include in blocks. Fee structures vary:
- Gas Fees: Users pay for computational resources (Ethereum)
- Priority Fees: Extra payments for faster transaction processing
- MEV (Maximal Extractable Value): Profits from transaction ordering
Types of Staking: Complete Overview
1. Native (Solo) Staking
Running your own validator node gives you maximum control and rewards but requires technical expertise and significant capital.
Requirements for Native Staking
Ethereum 2.0 Example:
- Minimum Stake: 32 ETH (~$75,000 at current prices)
- Hardware: Dedicated computer with reliable internet
- Technical Skills: Command line, server management, security practices
- Uptime: 99%+ availability to avoid penalties
Advantages:
- Maximum rewards (no commission fees)
- Full control over validator operations
- Direct contribution to network decentralisation
- Governance voting rights
Disadvantages:
- High capital requirements
- Technical complexity and maintenance
- Slashing risk from operational mistakes
- No liquidity during staking period
2. Delegated Staking
Most popular method where you delegate your tokens to existing validators while retaining ownership.
Popular Delegated Staking Networks
- Cardano (ADA): 4.5-5.2% APY, no minimum, no lock-up
- Solana (SOL): 6.8-7.5% APY, ~2.5 day unbonding
- Cosmos (ATOM): 10-14% APY, 21-day unbonding
- Polkadot (DOT): 10-14% APY, 28-day unbonding
- Tezos (XTZ): 5-6% APY, flexible delegation
3. Liquid Staking (Revolutionary Innovation)
Liquid staking protocols solve the liquidity problem by issuing derivative tokens representing your staked assets.
How Liquid Staking Works
- Deposit: Send ETH to liquid staking protocol
- Receive Derivative: Get stETH, rETH, or similar token
- Earn Rewards: Derivative token appreciates or rebases
- Maintain Liquidity: Trade derivative on DEXs anytime
- Compound: Use derivative in other DeFi protocols
Leading Liquid Staking Protocols
Lido Finance (Market Leader)
- Assets: ETH, SOL, MATIC, DOT
- TVL: $25+ billion
- Token: stETH (rebasing) or wstETH (wrapped)
- Yield: ~3.8% APY on ETH
- Pros: Largest liquidity, DeFi integration
- Cons: centralisation concerns, smart contract risk
Rocket Pool (decentralised Alternative)
- Assets: ETH only
- TVL: $3+ billion
- Token: rETH (appreciating)
- Yield: ~3.5% APY on ETH
- Pros: More decentralised, permissionless
- Cons: Smaller liquidity, higher complexity
4. CeFi Staking (Centralised Platforms)
Cryptocurrency exchanges and lending platforms offer simplified staking services.
Popular CeFi Staking Platforms
- Assets: 100+ cryptocurrencies
- Yield: 1-20% APY depending on asset
- Flexibility: Flexible and locked staking options
- Minimum: As low as $1
- Assets: ETH, ADA, SOL, ATOM, XTZ
- Yield: 2-5% APY (lower than native)
- Regulation: US-regulated, FDIC insurance on USD
- Ease: One-click staking
Comprehensive Risk & Reward Analysis
Staking Rewards by Network (2025)
| Network | APY Range | Lock-up Period | Minimum Stake |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethereum 2.0 | 3.2-4.1% | Until withdrawals enabled | 32 ETH (solo) / 0.01 ETH (pools) |
| Cardano | 4.5-5.2% | None | 10 ADA |
| Solana | 6.8-7.5% | 2.5 days | 0.01 SOL |
| Polkadot | 10-14% | 28 days | 1 DOT (pools) |
| Cosmos | 10-14% | 21 days | 0.1 ATOM |
| Avalanche | 8-11% | 2 weeks to 1 year | 25 AVAX |
Detailed Risk Analysis
1. Slashing Risk
Validators can lose part of their stake for malicious or negligent behaviour:
Common Slashing Conditions:
- Double Signing: Validator signs conflicting blocks
- Downtime: Extended periods offline (varies by network)
- Invalid Attestations: Voting for incorrect chain state
- Equivocation: Contradictory messages to the network
2. Smart Contract and Protocol Risks
DeFi staking protocols introduce additional technical risks:
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities:
- Code Bugs: Programming errors leading to fund loss
- Economic Exploits: Manipulation of protocol mechanics
- Governance Attacks: Malicious protocol changes
- Oracle Failures: Price feed manipulation
3. Market and Liquidity Risks
Cryptocurrency volatility affects staking returns:
Price Volatility Impact:
- Positive Scenario: 5% staking yield + 50% price appreciation = 55% total return
- Negative Scenario: 5% staking yield - 30% price decline = -25% total return
- Stable Scenario: 5% staking yield + 0% price change = 5% total return from staking rewards only
Best Staking Platforms 2025: Detailed Comparison
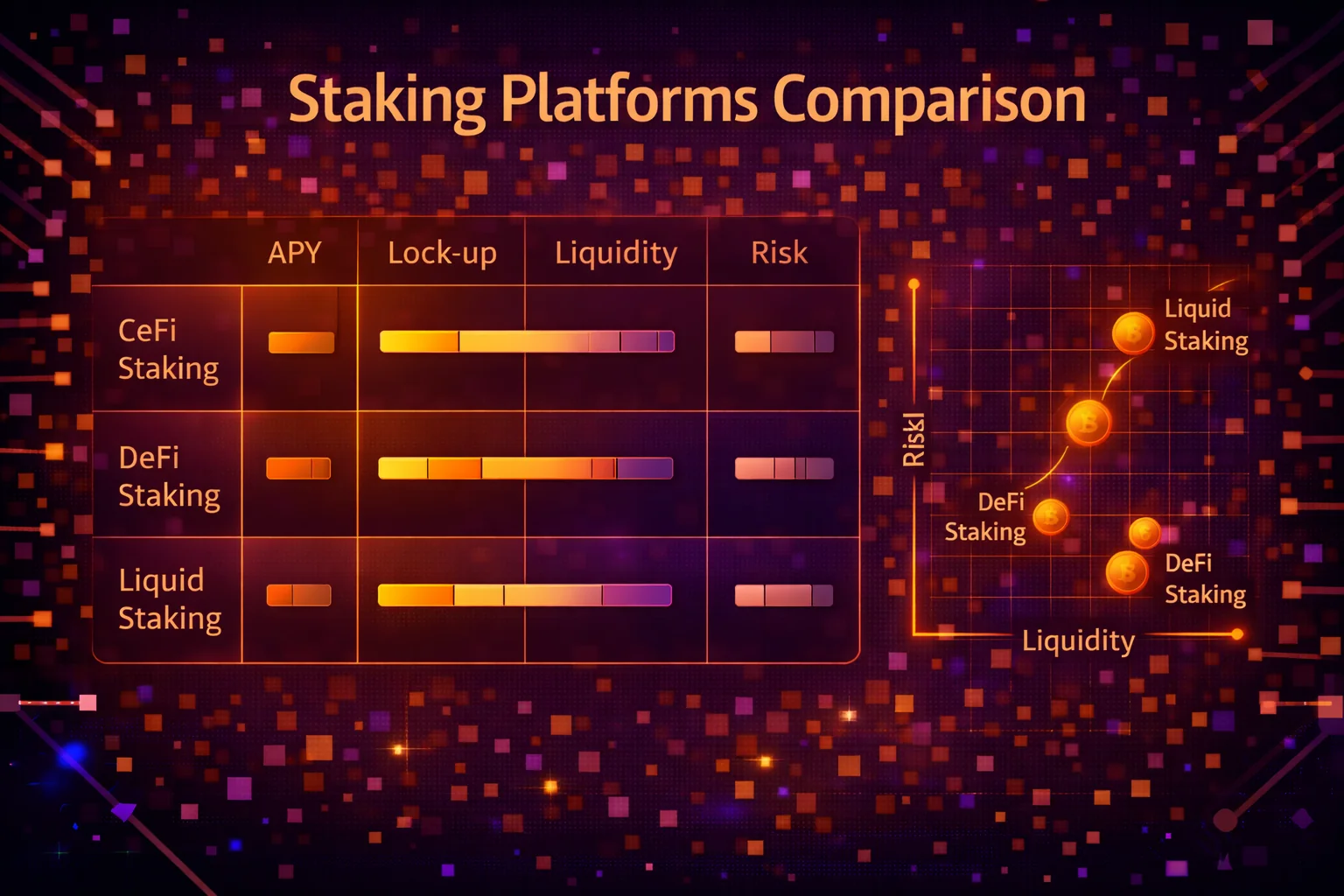
Liquid Staking Leaders
Lido Finance - Market Dominator
Overview: The largest liquid staking protocol with over $25 billion TVL
Supported Assets:
- Ethereum (stETH) - 3.8% APY
- Solana (stSOL) - 6.5% APY
- Polygon (stMATIC) - 4.2% APY
- Polkadot (stDOT) - 12% APY
Rocket Pool - decentralised Alternative
Overview: Community-driven protocol emphasizing decentralisation
Key Features:
- Permissionless node operation
- Distributed validator set
- rETH appreciates against ETH over time
- Lower protocol fees (0.05% vs Lido's 10%)
CeFi Staking Champions
Binance Earn - Comprehensive Platform
Staking Options:
- Flexible Savings: 1-8% APY, withdraw anytime
- Locked Staking: Higher yields for fixed terms
- DeFi Staking: Access to external protocols
For comprehensive platform comparisons and staking strategies, explore our staking platform comparison.
Coinbase Earn - Beginner Friendly
Advantages for Beginners:
- One-click staking activation
- FDIC insurance on USD balances
- Educational resources
- Regulatory compliance in US
Advanced Staking Strategies
Portfolio Allocation Models
Strategic approaches to building a diversified staking portfolio:
Conservative Model (Low Risk)
- 40% Ethereum: Liquid staking through Lido or Rocket Pool
- 30% Cardano: Native delegation, no lock-up
- 20% Solana: High-quality validators, short unbonding
- 10% Stablecoins: CeFi platforms for steady yield
- Target APY: 4-6% with lower volatility
Balanced Model (Moderate Risk)
- 25% Ethereum: Mix of liquid and native staking
- 20% Cardano: Multiple pool delegation
- 20% Solana: Diversified validator selection
- 15% Polkadot: Nomination pools
- 10% Cosmos: Hub and ecosystem tokens
- 10% Emerging Networks: Higher risk/reward protocols
- Target APY: 6-10% with moderate volatility
Aggressive Model (High Risk)
- 20% Ethereum: Leveraged liquid staking strategies
- 15% Solana: MEV-optimised validators
- 15% Polkadot: Parachain staking
- 15% Cosmos: High-yield ecosystem tokens
- 15% Avalanche: Subnet validation
- 10% Near Protocol: Emerging DeFi integration
- 10% Experimental: New protocols and testnets
- Target APY: 10-20% with high volatility
Yield optimisation Techniques
Compound Staking Strategies
Automated Compounding:
- Platform Selection: Choose platforms with auto-compounding
- Frequency optimisation: Balance gas costs vs compound frequency
- Threshold Management: Set minimum amounts before compounding
- Tax Efficiency: Consider tax implications of frequent compounding
Manual Compounding optimisation:
- Gas Price Monitoring: Compound during low-fee periods
- Batch Operations: Combine multiple actions in single transaction
- Cross-Chain Arbitrage: Move rewards to higher-yield opportunities
- Seasonal Timing: optimise for tax year and market cycles
Multi-Chain Yield Farming
Cross-Chain Opportunities:
- Bridge Strategies: Move assets to chains with higher yields
- Ecosystem Tokens: Stake native tokens on their home chains
- Liquid Staking Arbitrage: Trade liquid staking tokens across chains
- Governance Participation: Earn additional rewards through voting
Risk Management Framework
Diversification Strategies
Network Diversification:
- Consensus Mechanisms: Mix PoS variants (PBFT, DPoS, NPoS)
- Geographic Distribution: Validators in different regions
- Development Teams: Avoid concentration in single foundation
- Use Case Diversity: Smart contracts, payments, DeFi, gaming
Validator Diversification:
- Performance Metrics: Mix of high and moderate performers
- Commission Rates: Balance low fees with sustainability
- Stake Distribution: Avoid over-concentrated validators
- Infrastructure Diversity: Different hosting providers and locations
Hedging Strategies
Price Risk Mitigation:
- Stablecoin Allocation: Maintain 10-20% in stable assets
- Derivatives Hedging: Use futures or options to hedge price risk
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: Regular staking regardless of price
- Profit Taking: Systematic reward harvesting during bull markets
Tax-Efficient Staking
Jurisdiction optimisation
Tax-Friendly Locations:
- Portugal: No capital gains tax on crypto (as of 2025)
- Singapore: No capital gains tax for individuals
- Switzerland: Favorable crypto tax treatment
- Puerto Rico: US territory with crypto tax incentives
Timing Strategies
Tax Year optimisation:
- Reward Timing: Claim rewards in low-income years
- Loss Harvesting: realise losses to offset staking income
- Long-Term Holding: Qualify for capital gains treatment
- Entity Structures: Consider corporate or trust structures
Getting Started with Staking
Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
- Choose Your Approach: Decide between CeFi simplicity or DeFi control
- Select Assets: Start with major networks (ETH, ADA, SOL)
- Pick Platform: Research fees, security, and reputation
- Start Small: Begin with 5-10% of your crypto portfolio
- Monitor Performance: Track rewards and validator performance
- Diversify: Spread across multiple validators and networks
Platform Selection Framework
Choose Based on Your Profile
Complete Beginner:
- Start with Coinbase Earn or Binance Earn
- Focus on major assets (ETH, ADA, SOL)
- Begin with small amounts to learn
Intermediate User:
- Explore Lido for liquid staking
- Try native delegation on Cardano or Solana
- Diversify across multiple platforms
Advanced User:
- Consider solo staking for maximum rewards
- Use Rocket Pool for decentralised liquid staking
- Explore smaller networks for higher yields
Staking Market Analysis 2025
Total Value Locked (TVL) in Staking
The staking market has experienced explosive growth, with total staked value exceeding $150 billion across all networks in 2025:
Market Leaders by TVL
- Ethereum: $45+ billion staked (28% of total supply)
- Solana: $25+ billion staked (65% of total supply)
- Cardano: $18+ billion staked (70% of total supply)
- Polkadot: $8+ billion staked (55% of total supply)
- Cosmos: $6+ billion staked (60% of total supply)
Institutional Adoption Trends
Institutional participation in staking has grown significantly:
Major Institutional Players
- Coinbase: $8+ billion in customer staking assets
- Kraken: $4+ billion in staking services
- Binance: $12+ billion across multiple staking products
- Lido: $25+ billion in liquid staking protocols
- Traditional Finance: Banks and asset managers entering space
Regulatory Developments
- United States: SEC guidance on staking services
- European Union: MiCA regulation covering staking providers
- United Kingdom: FCA framework for crypto staking
- Asia-Pacific: Varied approaches across jurisdictions
Technology Evolution
Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSDs)
Liquid staking has revolutionised the staking landscape:
- Market Size: $35+ billion in liquid staking tokens
- DeFi Integration: LSDs used as collateral across protocols
- Yield Stacking: Earning staking rewards plus DeFi yields
- Composability: Building complex financial products
Restaking Innovation
EigenLayer and similar protocols enable restaking for additional yields:
- Concept: Reuse staked ETH to secure other protocols
- Additional Rewards: Earn from multiple services simultaneously
- Increased Risk: Additional slashing conditions
- Market Potential: $10+ billion TVL expected by end of 2025
Future Outlook
Network Upgrades and Improvements
- Ethereum: Continued scaling with Layer 2 integration
- Cardano: Hydra scaling and governance improvements
- Solana: Network stability and validator improvements
- Polkadot: Parachain slot auctions and cross-chain features
Emerging Trends
- Cross-chain staking: Stake assets on multiple chains
- AI-optimised staking: Automated validator selection
- ESG considerations: Environmental impact of different consensus mechanisms
- Institutional products: Custody and compliance solutions
Security and Best Practices
Validator Selection Criteria
Choosing the right validator is crucial for maximising rewards and minimising risks:
Performance Metrics
- Uptime: Look for 99%+ uptime history
- Commission rates: Balance low fees with sustainability
- Stake size: Avoid over-concentrated validators
- Slashing history: Check for past penalties
- Community reputation: Research validator background
Infrastructure Assessment
- Geographic distribution: Validators in different regions
- Hardware specifications: Enterprise-grade equipment
- Redundancy: Backup systems and failover procedures
- Security practices: Key management and access controls
- Monitoring: 24/7 network monitoring and alerting
Smart Contract Risk Assessment
Protocol Evaluation Framework
- Code audits: Multiple independent security audits
- Bug bounty programs: Active security researcher engagement
- Time in operation: Battle-tested protocols preferred
- TVL and adoption: Market validation and liquidity
- Governance structure: decentralised decision-making
Insurance and Protection
- Protocol insurance: Some platforms offer slashing protection
- DeFi insurance: Third-party coverage for smart contract risks
- Self-insurance: Diversification as risk mitigation
- Emergency procedures: Protocol pause and upgrade mechanisms
Operational Security
Key Management
- Hardware wallets: Use for validator key storage
- Multi-signature: Require multiple signatures for operations
- Key rotation: Regular key updates for long-term security
- Backup procedures: Secure key backup and recovery
Monitoring and Alerting
- Performance tracking: Monitor validator performance metrics
- Reward monitoring: Track expected vs actual rewards
- Network alerts: Stay informed about network upgrades
- Security notifications: Monitor for potential threats
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Energy Efficiency of Proof-of-Stake
One of the most significant advantages of staking over mining is its dramatically lower environmental impact:
Energy Consumption Comparison
- Bitcoin (PoW): ~150 TWh annually (comparable to Argentina)
- Ethereum (PoS): ~0.0026 TWh annually (99.95% reduction)
- Cardano: ~6 GWh annually (equivalent to 600 homes)
- Solana: ~3.8 GWh annually (ultra-efficient consensus)
Carbon Footprint Analysis
The transition to proof-of-stake has significant environmental benefits:
- Ethereum's Merge: Reduced global crypto carbon emissions by ~0.2%
- Validator Efficiency: Single validator node can process thousands of transactions
- Renewable Energy: Many validators powered by renewable sources
- ESG Compliance: Institutional investors increasingly prefer PoS networks
Sustainable Staking Practices
Green Validator Selection
- Renewable Energy: Choose validators powered by solar, wind, or hydro
- Carbon Neutral: Validators with carbon offset programs
- Efficiency Metrics: Hardware optimisation and energy monitoring
- Geographic Distribution: Validators in regions with clean energy grids
Protocol-Level Sustainability
- Algorand: Carbon-negative blockchain through offset partnerships
- Tezos: Energy-efficient consensus with minimal hardware requirements
- Cardano: Peer-reviewed research focusing on sustainability
- Ethereum: Ongoing research into further efficiency improvements
Global Adoption and Regional Differences
Regional Staking Preferences
North America
- Regulatory Focus: Compliance-first approach with regulated platforms
- Popular Platforms: Coinbase, Kraken, institutional custody solutions
- Tax Considerations: Complex reporting requirements drive platform choice
- Institutional Adoption: Pension funds and endowments entering space
Europe
- MiCA Regulation: Comprehensive framework for staking services
- DeFi Preference: Higher adoption of decentralised protocols
- Environmental Focus: Strong preference for sustainable PoS networks
- Cross-Border: Seamless staking across EU member states
Asia-Pacific
- High Yields: Preference for higher-risk, higher-reward staking
- Mobile-First: Smartphone-based staking applications
- Local Networks: Strong support for regional blockchain projects
- Retail Adoption: Mass market participation in staking
Emerging Market Opportunities
Financial Inclusion
- Banking Alternative: Staking as alternative to traditional savings
- Inflation Hedge: Protection against local currency devaluation
- Remittances: Cross-border value transfer through staking
- Microfinance: Small-scale staking for economic empowerment
Infrastructure Development
- Validator Networks: Local validator infrastructure development
- Educational Programs: Blockchain literacy and staking education
- Regulatory Frameworks: Progressive crypto-friendly regulations
- Technology Access: Mobile-first solutions for smartphone users
Institutional Staking Solutions
Enterprise Staking Requirements
Compliance and Custody
- Qualified Custody: Regulated custodians for institutional assets
- Audit Trails: Comprehensive transaction and reward tracking
- Risk Management: Sophisticated risk assessment and mitigation
- Reporting: Detailed performance and compliance reporting
Operational Infrastructure
- Multi-Signature: Enterprise-grade key management systems
- Redundancy: Geographically distributed validator infrastructure
- Monitoring: 24/7 network monitoring and alerting systems
- Insurance: Comprehensive coverage for operational risks
Institutional Service Providers
Traditional Finance Integration
- Fidelity Digital Assets: Institutional custody and staking
- State Street: Digital asset services for institutions
- Northern Trust: Custody and administration services
- BNY Mellon: Digital asset custody and staking solutions
Crypto-Native Providers
- Coinbase Institutional: Prime brokerage and staking services
- Kraken Institutional: Professional trading and staking
- BitGo: Institutional custody and staking infrastructure
- Anchorage Digital: Federally chartered digital asset bank
Pension Fund and Endowment Adoption
Investment Thesis
- Diversification: Alternative asset class for portfolio balance
- Yield Generation: Attractive returns in low-interest environment
- Inflation Protection: Hedge against currency debasement
- Long-term Perspective: Patient capital suitable for staking lock-ups
Implementation Challenges
- Regulatory Approval: Board and regulatory approval processes
- Risk Assessment: Comprehensive due diligence requirements
- Operational Complexity: Integration with existing systems
- Performance Measurement: Benchmarking and attribution analysis
Advanced Staking Economics and Market Dynamics
Tokenomics and Inflation Mechanisms
Understanding the economic models behind different proof-of-stake networks is crucial for making informed staking decisions. Each network implements unique tokenomics that directly impact staking rewards, token value, and long-term sustainability. These economic mechanisms determine how new tokens are created, distributed, and potentially burnt, affecting both staking yields and the underlying asset's value proposition.
Ethereum's post-merge economics feature a deflationary mechanism where transaction fees are burnt, potentially reducing the total supply over time. This creates a unique dynamic where staking rewards come from new issuance, but high network activity can make ETH deflationary overall. The base fee burning mechanism means that during periods of high network usage, more ETH is burnt than issued, creating deflationary pressure that can enhance the value of staked positions beyond just staking rewards.
Cardano implements a treasury system where a portion of transaction fees and monetary expansion funds ecosystem development and governance initiatives. This creates a sustainable funding mechanism for protocol development while providing predictable staking rewards. The treasury system ensures long-term network sustainability by funding research, development, and community initiatives that enhance the protocol's value proposition and adoption potential.
Network Effects and Staking Participation Rates
The percentage of tokens staked on a network significantly impacts both security and economics. Higher staking participation rates generally increase network security by making attacks more expensive, but they can also reduce individual staking yields as rewards are distributed amongst more participants. Understanding these dynamics helps stakeholders make strategic decisions about when and how much to stake based on current participation levels and expected changes.
Solana maintains high staking participation rates of approximately 65-70% of total supply, which provides strong network security but results in moderate individual yields. The high participation rate reflects confidence in the network's long-term prospects and the attractiveness of staking rewards relative to other opportunities. However, this also means that new stakers enter a competitive environment where yields may be lower than networks with less participation.
Polkadot's nomination pools system creates interesting dynamics where the number of active validators is limited, but the total stake backing them can vary significantly. This creates opportunities for strategic staking where choosing the right validators and timing entries and exits can significantly impact returns. The limited validator set ensures high-quality infrastructure while the nomination system allows broad participation in network security.
Liquid Staking Market Dynamics and Competition
The liquid staking market has evolved into a competitive landscape where different protocols compete on yield, decentralisation, and integration capabilities. Understanding these competitive dynamics is essential for choosing the right liquid staking provider and anticipating future market developments. The competition drives innovation in areas like MEV optimisation, validator selection algorithms, and DeFi integration capabilities.
Lido's market dominance in liquid staking creates both opportunities and concerns. Whilst their large scale enables better MEV extraction and lower fees, it also raises centralisation concerns that could impact Ethereum's decentralisation. The protocol's governance token (LDO) allows stakeholders to participate in decisions about validator selection, fee structures, and protocol upgrades, creating additional value beyond just staking rewards.
Rocket Pool's decentralised approach attracts users who prioritise decentralisation over maximum yields. Their permissionless validator system allows anyone to run a validator with just 16 ETH plus RPL tokens, creating a more distributed validator set. This approach may result in slightly lower yields compared to more centralised alternatives, but it provides better alignment with Ethereum's decentralisation goals and potentially lower regulatory risk.
Cross-Chain Staking Opportunities and Arbitrage
The multi-chain ecosystem creates opportunities for sophisticated staking strategies that leverage differences in yields, tokenomics, and market conditions across different networks. Cross-chain staking strategies require understanding bridge risks, transaction costs, and timing considerations, but they can provide enhanced returns for experienced participants willing to manage additional complexity.
Cosmos ecosystem tokens often provide higher staking yields than Ethereum or Bitcoin-based networks, but they come with additional risks including smaller market caps, less liquidity, and higher volatility. The Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol enables sophisticated strategies where assets can be moved between Cosmos chains to optimise yields while maintaining exposure to the broader ecosystem's growth potential.
Avalanche's subnet architecture creates unique staking opportunities where validators can participate in securing multiple subnets simultaneously, potentially earning rewards from multiple sources. This creates complex optimisation problems where validators must balance hardware requirements, token holdings, and expected returns across different subnets. The subnet model also enables application-specific blockchains with customised staking parameters and reward structures.
Regulatory Impact on Staking Economics
Regulatory developments significantly impact staking economics through taxation, compliance requirements, and operational restrictions. Understanding the regulatory landscape is crucial for long-term staking strategies, particularly for institutional participants and high-net-worth individuals who may face additional compliance obligations. Regulatory clarity can also drive institutional adoption, potentially increasing demand for staking services and infrastructure.
The European Union's Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation provides a comprehensive framework for staking services, requiring providers to meet specific operational and financial requirements. This regulatory clarity enables traditional financial institutions to offer staking services while providing consumer protections. However, compliance costs may reduce yields or limit service availability in certain jurisdictions.
United States regulatory uncertainty around staking services has created market fragmentation where different providers offer varying levels of service based on their regulatory interpretation and risk tolerance. The SEC's enforcement actions and guidance statements significantly impact how staking services are structured and marketed, affecting both yields and accessibility for US-based participants.
Future Evolution of Staking Mechanisms
The staking landscape continues evolving with new consensus mechanisms, reward structures, and participation models that could significantly impact future opportunities. Understanding these developments helps stakeholders prepare for changes and identify emerging opportunities before they become mainstream. Innovation in areas like shared security, restaking, and cross-chain validation could create new categories of staking opportunities.
EigenLayer's restaking protocol represents a significant innovation that allows ETH stakers to opt into additional validation duties for other protocols, earning additional rewards while taking on additional slashing risks. This creates a new category of "actively validated services" that could significantly expand the utility and rewards available to staked ETH while introducing new risk management considerations.
Shared security models like those being developed for Cosmos and Polkadot could enable smaller chains to leverage the security of larger networks while providing additional staking opportunities for validators. These models could reduce the barriers to launching new blockchains while creating new revenue streams for existing validators and stakers.
Practical Implementation Guidelines
Cryptocurrency staking education requires a comprehensive understanding of consensus mechanisms, validator operations, and reward distribution systems that govern proof-of-stake networks. Effective staking knowledge combines technical concepts with practical implementation strategies to maximise rewards while minimising risks associated with validator selection and network participation.
Step-by-Step Execution Framework
Strategic staking implementation begins with comprehensive planning that includes validator research, staking setup, and reward optimisation procedures. Professional stakers establish clear protocols for validator selection, delegation management, and reward claiming schedules that maintain consistency while allowing flexibility for validator switching and changing network conditions.
Security and Operational Procedures
Robust staking security frameworks encompass validator verification, delegation protection, and secure backup procedures that protect against both technical failures and staking security breaches. Professional stakers implement comprehensive operational security protocols including validator monitoring procedures, slashing protection systems, and emergency unstaking plans.
Performance Tracking and optimisation
Staking reward tracking requires specialised methodologies that account for validator performance, network conditions, and compound interest calculations. Regular staking evaluation enables strategy optimisation and validator selection while maintaining alignment with yield objectives and risk tolerance parameters.
Staking Technology Evolution
New staking mechanisms and protocols continue emerging with enhanced features and security improvements that benefit both validators and delegators through innovative consensus algorithms and reward distribution systems. Advanced staking technologies incorporate sophisticated risk management tools, automated optimisation features, and enhanced security protocols that provide superior staking experiences for professional cryptocurrency investors seeking optimal yield generation strategies through innovative technological solutions and comprehensive staking frameworks.
Final Summary
Cryptocurrency staking represents one of the most accessible and sustainable methods for generating passive income in the digital asset ecosystem. By understanding the fundamental mechanics, risks, and reward structures, investors can make informed decisions about incorporating staking into their cryptocurrency investment strategies.
The evolution of staking from simple proof-of-stake validation to sophisticated liquid staking protocols and DeFi integration demonstrates the maturation of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Modern staking options provide flexibility, competitive yields, and enhanced security features that make passive income generation more accessible to mainstream investors.
Success in cryptocurrency staking requires careful platform selection, understanding of lock-up periods and slashing risks, and ongoing monitoring of market conditions and protocol developments. By starting with established platforms and gradually exploring more advanced strategies, investors can build sustainable passive income streams while contributing to network security and decentralisation.
As the cryptocurrency market continues evolving, staking will likely become an increasingly important component of diversified digital asset portfolios. The combination of technological innovation, regulatory clarity, and institutional adoption suggests that staking rewards will remain a viable long-term strategy for cryptocurrency investors seeking passive income opportunities in the growing digital economy.
Conclusion
Crypto staking has evolved from a niche activity to a cornerstone of the digital asset ecosystem. With over $150 billion staked across various networks in 2025, staking represents one of the most significant developments in blockchain technology since the introduction of smart contracts.
Key Takeaways
- Accessibility: Staking is now accessible to everyone, from beginners using CeFi platforms to advanced users running their own validators
- Innovation: Liquid staking and restaking protocols have unlocked new possibilities for yield generation and capital efficiency
- Maturation: The market has matured with institutional adoption, regulatory clarity, and improved security practices
- Diversification: Multiple staking methods and networks provide options for different risk tolerances and investment goals
- Sustainability: Proof-of-stake networks offer environmentally sustainable alternatives to energy-intensive mining
- Global Impact: Staking is driving financial inclusion and infrastructure development worldwide
Looking Ahead
The staking landscape will continue evolving with:
- Cross-chain integration: Seamless staking across multiple blockchain networks
- Institutional products: More sophisticated tools for professional investors
- Regulatory frameworks: Clearer guidelines providing certainty for market participants
- Technology improvements: Better user experiences and enhanced security features
- Environmental leadership: Continued focus on sustainable blockchain infrastructure
- Financial innovation: New products combining staking with traditional finance
Whether you're seeking passive income, supporting network decentralisation, or exploring new financial primitives, staking offers compelling opportunities in the evolving crypto ecosystem. Start with small amounts, understand the risks, and gradually build your staking portfolio as you gain experience and confidence.
The future of finance is being built on proof-of-stake networks, and by participating in staking, you're not just earning rewards – you're helping to secure and decentralise the infrastructure of tomorrow's financial system.
Final Recommendations
As you embark on your staking journey, remember these essential principles: diversify across multiple networks and platforms to reduce risk, stay informed about protocol updates and market developments, prioritise security through proper key management and platform selection, and maintain a long-term perspective that aligns with your financial goals.
The staking ecosystem in 2025 offers something for everyone, from simple liquid staking solutions that provide immediate liquidity to advanced restaking protocols that maximise yield potential. By understanding the fundamentals covered in this guide and staying engaged with the rapidly evolving landscape, you'll be well-positioned to capitalise on the opportunities that staking presents while contributing to the growth and security of decentralised networks.
Sources & References
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is crypto staking?
- Crypto staking is the process of locking up digital assets to help secure a blockchain network and earn rewards. It's the foundation of proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms, where validators are chosen to create new blocks based on their stake size and other factors.
- Is staking safe?
- Staking carries risks such as slashing (penalties for validator misbehaviour), protocol bugs, and asset volatility. However, using reputable providers, diversifying across validators, and understanding the risks can help minimise potential losses. The risk level varies significantly between different networks and staking methods.
- Which are the best staking platforms in 2025?
- Popular staking platforms in 2025 include Lido (liquid staking leader), Rocket Pool (decentralised alternative), Binance Earn (comprehensive CeFi), and Coinbase (beginner-friendly). Each has trade-offs in yield, risk, decentralisation, and ease of use. The best choice depends on your experience level and priorities.
- Can I lose money staking crypto?
- Yes, you can lose money through asset price decline, slashing penalties, smart contract bugs, or opportunity costs during lock-up periods. If ETH drops 30%, your staking rewards won't offset the loss. Validators can lose 0.5-100% of stake for misbehaviour, and DeFi protocols can be exploited.
- What's the difference between liquid staking and regular staking?
- Regular staking locks tokens with no liquidity. Liquid staking provides tradable derivative tokens representing staked assets, allowing trading and DeFi usage. You can trade the derivative token anytime, use it as collateral, earn additional yields, and avoid long unbonding periods.
- How much can I earn from staking?
- Staking yields vary: Ethereum 3.2-4.1%, Cardano 4.5-5.2%, Solana 6.8-7.5%, Polkadot 10-14%. Higher yields often come with higher risks. Returns depend on network conditions, validator performance, and market volatility.
- Do I need technical knowledge to stake?
- It depends: CeFi platforms require no technical knowledge, while solo staking requires advanced technical expertise. Liquid staking needs basic DeFi understanding, and native delegation requires moderate technical skills.
- What's the minimum amount needed to start staking?
- Minimums vary: Ethereum solo staking requires 32 ETH (~$75,000), liquid staking starts at 0.01 ETH (~$25), CeFi platforms often as low as $1. Cardano needs 10 ADA (~$5), Solana 0.01 SOL (~$2).
- How often are staking rewards paid?
- Frequency varies: Ethereum every 6.4 minutes, Cardano every 5 days, Solana every 2-3 days, Polkadot every 24 hours, CeFi platforms daily or weekly. Reward distribution depends on network consensus mechanisms and platform policies.
- Is staking income taxable?
- Generally yes - staking rewards are often taxed as ordinary income when received, with capital gains tax applying when sold. Tax treatment varies by jurisdiction. Track all rewards and their fair market value, and consult tax professionals for your situation.
← Back to Crypto Investing Blog Index
Financial Disclaimer
This content is not financial advice. All information provided is for educational purposes only. Cryptocurrency investments carry significant investment risk, and past performance does not guarantee future results. Always do your own research and consult a qualified financial advisor before making investment decisions.